import xarray as xr
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import urllib.request
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
import warnings
#warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')Summary
This example is based on the OceanWatch tutorial meterial edited with Great Lakes satellite data.In this example you will see how to extract Great Lakes ice concentration data from the ERDDAP server and make a ice concentration map, and caculate the monthly
The example demonstrates the following techniques:
- Loading Great Lakes ice concentration data from Great Lakes ERDDAP data server.
- Create a map of ice concentration.
- Compute the daily mean over the selected region.
Datesets used:
- Great Lakes ice concentration: Great Lakes ice concentration product.
Import the required Python modules
Downlading data from ERDDAP server
Because ERDDAP includes RESTful services, you can download data listed on any ERDDAP platform from Python using the URL structure. For example, the following link allows you to subset daily ice concentration data from the dataset GL_Ice_Concentration_GCS
In this specific example, we will get the SST data from 2023-06-01 to 2023-06-30. the URL we generated is :
https://apps.glerl.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/GL_Ice_Concentration_GCS.nc?ice_concentration%5B(1995-01-01T12:00:00Z):1:(2024-05-01T12:00:00Z)%5D%5B(41.38):1:(42.10)%5D%5B(-83.59):1:(-82.5)%5D
we extract the data in csv format due to the nc library not available.
url="https://apps.glerl.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/GL_Ice_Concentration_GCS.nc?ice_concentration%5B(1995-01-01T12:00:00Z):1:(2024-05-01T12:00:00Z)%5D%5B(41.38):1:(42.10)%5D%5B(-83.59):1:(-82.5)%5D"
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, "w_e_ice_concentration.nc")('w_e_ice_concentration.nc', <http.client.HTTPMessage at 0x1b687bf22d0>)Importing NetCDF4 data in Python
Now that we’ve downloaded the data locally, we can import it and extract our variables of interest.
The xarray package makes it very convenient to work with NetCDF files. Documentation is available here: http://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/why-xarray.html
import xarray as xr
import netCDF4 as ncOpen the file and load it as an xarray dataset:
ds = xr.open_dataset('w_e_ice_concentration.nc',decode_cf=False)
#ds = xr.open_dataset('e_sst.nc')Examine the data structure:
ds<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (time: 7146, latitude: 52, longitude: 79)
Coordinates:
* time (time) float64 7.89e+08 7.89e+08 ... 1.714e+09 1.715e+09
* latitude (latitude) float64 41.38 41.4 41.41 ... 42.07 42.08 42.1
* longitude (longitude) float64 -83.59 -83.58 -83.56 ... -82.51 -82.5
Data variables:
ice_concentration (time, latitude, longitude) float32 ...
Attributes: (12/28)
cdm_data_type: Grid
Conventions: CF-1.6, COARDS, ACDD-1.3
Easternmost_Easting: -82.496964466524
GDAL: GDAL 3.4.3, released 2022/04/22
geospatial_lat_max: 42.0985561800016
geospatial_lat_min: 41.3837647963109
... ...
standard_name_vocabulary: CF Standard Name Table v29
summary: Ice Concentration from Great Lakes Surface En...
time_coverage_end: 2024-05-01T12:00:00Z
time_coverage_start: 1995-01-01T12:00:00Z
title: Ice Concentration from Great Lakes Surface En...
Westernmost_Easting: -83.590174818051Examine which coordinates and variables are included in the dataset:
ds.dimsFrozen({'time': 7146, 'latitude': 52, 'longitude': 79})ds.coordsCoordinates:
* time (time) float64 7.89e+08 7.89e+08 ... 1.714e+09 1.715e+09
* latitude (latitude) float64 41.38 41.4 41.41 41.43 ... 42.07 42.08 42.1
* longitude (longitude) float64 -83.59 -83.58 -83.56 ... -82.52 -82.51 -82.5ds.data_varsData variables:
ice_concentration (time, latitude, longitude) float32 ...ds.attrs{'cdm_data_type': 'Grid',
'Conventions': 'CF-1.6, COARDS, ACDD-1.3',
'Easternmost_Easting': -82.496964466524,
'GDAL': 'GDAL 3.4.3, released 2022/04/22',
'geospatial_lat_max': 42.0985561800016,
'geospatial_lat_min': 41.3837647963109,
'geospatial_lat_resolution': 0.014015517327269056,
'geospatial_lat_units': 'degrees_north',
'geospatial_lon_max': -82.496964466524,
'geospatial_lon_min': -83.590174818051,
'geospatial_lon_resolution': 0.01401551732726889,
'geospatial_lon_units': 'degrees_east',
'history': 'Ice concentration from Great Lakes Surface Environmental Analysis (GLSEA) asc format to nc fromat\n2024-09-18T16:53:43Z (local files)\n2024-09-18T16:53:43Z https://apps.glerl.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/GL_Ice_Concentration_GCS.nc?ice_concentration%5B(1995-01-01T12:00:00Z):1:(2024-05-01T12:00:00Z)%5D%5B(41.38):1:(42.10)%5D%5B(-83.59):1:(-82.5)%5D',
'infoUrl': 'https://coastwatch.glerl.noaa.gov/glsea/glsea.html',
'institution': 'CoastWatch Great Lakes Node',
'keywords': 'analysis, concentration, data, distribution, environmental, glsea, great, great lakes, ice, ice distribution, ice_concentration, lakes, nic, surface, time',
'license': 'The data may be used and redistributed for free but is not intended\nfor legal use, since it may contain inaccuracies. Neither the data\nContributor, ERD, NOAA, nor the United States Government, nor any\nof their employees or contractors, makes any warranty, express or\nimplied, including warranties of merchantability and fitness for a\nparticular purpose, or assumes any legal liability for the accuracy,\ncompleteness, or usefulness, of this information.',
'NCO': 'netCDF Operators version 5.0.7 (Homepage = http://nco.sf.net, Code = https://github.com/nco/nco)',
'Northernmost_Northing': 42.0985561800016,
'source': 'Ice Concentration from Great Lakes Surface Environmental Analysis (GLSEA) and NIC, Geodetic coordinate system (LAT, LON), 1995-present',
'sourceUrl': '(local files)',
'Southernmost_Northing': 41.3837647963109,
'standard_name_vocabulary': 'CF Standard Name Table v29',
'summary': 'Ice Concentration from Great Lakes Surface Environmental Analysis (GLSEA) and NIC',
'time_coverage_end': '2024-05-01T12:00:00Z',
'time_coverage_start': '1995-01-01T12:00:00Z',
'title': 'Ice Concentration from Great Lakes Surface Environmental Analysis (GLSEA) and NIC, Geodetic coordinate system (LAT, LON), 1995-present',
'Westernmost_Easting': -83.590174818051}Examine the structure of ice concentration:
ds.ice_concentration.shape(7146, 52, 79)Our dataset is a 3-D array with 52 rows corresponding to latitudes and 79 columns corresponding to longitudes, for each of the 7146 time steps. #### Get the dates for each time step:
ds.time<xarray.DataArray 'time' (time: 7146)>
array([7.889616e+08, 7.890480e+08, 7.891344e+08, ..., 1.714392e+09,
1.714478e+09, 1.714565e+09])
Coordinates:
* time (time) float64 7.89e+08 7.89e+08 7.891e+08 ... 1.714e+09 1.715e+09
Attributes:
_CoordinateAxisType: Time
actual_range: [7.8896160e+08 1.7145648e+09]
axis: T
calendar: Gregorian
ioos_category: Time
long_name: Time
standard_name: time
time_origin: 01-JAN-1970 00:00:00
units: seconds since 1970-01-01T00:00:00Zds.time.attrs{'_CoordinateAxisType': 'Time',
'actual_range': array([7.8896160e+08, 1.7145648e+09]),
'axis': 'T',
'calendar': 'Gregorian',
'ioos_category': 'Time',
'long_name': 'Time',
'standard_name': 'time',
'time_origin': '01-JAN-1970 00:00:00',
'units': 'seconds since 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z'}print(ds.time)<xarray.DataArray 'time' (time: 7146)>
array([7.889616e+08, 7.890480e+08, 7.891344e+08, ..., 1.714392e+09,
1.714478e+09, 1.714565e+09])
Coordinates:
* time (time) float64 7.89e+08 7.89e+08 7.891e+08 ... 1.714e+09 1.715e+09
Attributes:
_CoordinateAxisType: Time
actual_range: [7.8896160e+08 1.7145648e+09]
axis: T
calendar: Gregorian
ioos_category: Time
long_name: Time
standard_name: time
time_origin: 01-JAN-1970 00:00:00
units: seconds since 1970-01-01T00:00:00ZThe time units is seconds, we need to convert the seconds to dates.
dates=nc.num2date(ds.time,ds.time.units,only_use_cftime_datetimes=False,
only_use_python_datetimes=True )
datesarray([real_datetime(1995, 1, 1, 12, 0), real_datetime(1995, 1, 2, 12, 0),
real_datetime(1995, 1, 3, 12, 0), ...,
real_datetime(2024, 4, 29, 12, 0),
real_datetime(2024, 4, 30, 12, 0),
real_datetime(2024, 5, 1, 12, 0)], dtype=object)Find the index of dates for 2019-03-01
for i, date in enumerate(dates):
if date.strftime("%Y-%m-%d") == "2019-03-01":
print(i, date)5872 2019-03-01 12:00:005872 is the index on the array dates for 2019-03-01.
Create a map of ice concentration for March 1, 2019 (our 5872th time step).
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
#np.warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')#### Examine the values of ice concentration:
print(ds.ice_concentration.values)
print(ds.ice_concentration.shape)[[[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. 0.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]]
[[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. 0.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]]
[[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. 0.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]]
...
[[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. 0.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]]
[[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. 0.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]]
[[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. 0.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]
[-99999. -99999. -99999. ... -99999. -99999. -99999.]]]
(7146, 52, 79)ds.ice_concentration.attrs{'_FillValue': -99999.0,
'colorBarMaximum': 100.0,
'colorBarMinimum': 0.0,
'colorBarPalette': 'WhiteBlack',
'grid_mapping': 'crs',
'ioos_category': 'Ocean Color',
'long_name': 'Ice Concentration',
'standard_name': 'ice_concentration',
'units': 'percent'}ds.ice_concentration.attrs['_FillValue']-99999.0Make a new ice concentration DataArray and replace _fillValue with NaN
nan_ice_concentration = ds.ice_concentration.where(ds.ice_concentration.values != ds.ice_concentration.attrs['_FillValue'])
print(nan_ice_concentration)<xarray.DataArray 'ice_concentration' (time: 7146, latitude: 52, longitude: 79)>
array([[[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, 0.],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]],
[[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, 0.],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]],
[[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, 0.],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
...
...,
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]],
[[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, 0.],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]],
[[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, 0.],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* time (time) float64 7.89e+08 7.89e+08 ... 1.714e+09 1.715e+09
* latitude (latitude) float64 41.38 41.4 41.41 41.43 ... 42.07 42.08 42.1
* longitude (longitude) float64 -83.59 -83.58 -83.56 ... -82.52 -82.51 -82.5
Attributes:
_FillValue: -99999.0
colorBarMaximum: 100.0
colorBarMinimum: 0.0
colorBarPalette: WhiteBlack
grid_mapping: crs
ioos_category: Ocean Color
long_name: Ice Concentration
standard_name: ice_concentration
units: percentSet some color breaks
# find min value in man_sst
np.nanmin(nan_ice_concentration)0.0np.nanmax(nan_ice_concentration)99.99847levs = np.arange(0, 101, 10)
len(levs)11Define a color palette
# init a color list
jet=["blue", "#007FFF", "cyan","#7FFF7F", "yellow", "#FF7F00", "red", "#7F0000"]Set color scale using the jet palette
cm = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('my_jet', jet, N=len(levs))plot the ice_concentration map
plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 5))
#plot 5872th ice concentration image: nan_ice_concentration[5872 ,:,:]
plt.contourf(nan_ice_concentration.longitude, nan_ice_concentration.latitude, nan_ice_concentration[5872,:,:], levs,cmap=cm)
#plot the color scale
plt.colorbar()
#example of how to add points to the map
#plt.scatter(np.linspace(-82,-80.5,num=4),np.repeat(42,4),c='black')
#example of how to add a contour line
#step = np.arange(9,26, 1)
#plt.contour(ds.longitude, ds.latitude, ds.sst[0,:,:],levels=step,linewidths=1)
#plot title
plt.title("West Lake Erie Ice Concentration - " + dates[5872].strftime('%b %d, %Y'))
plt.show()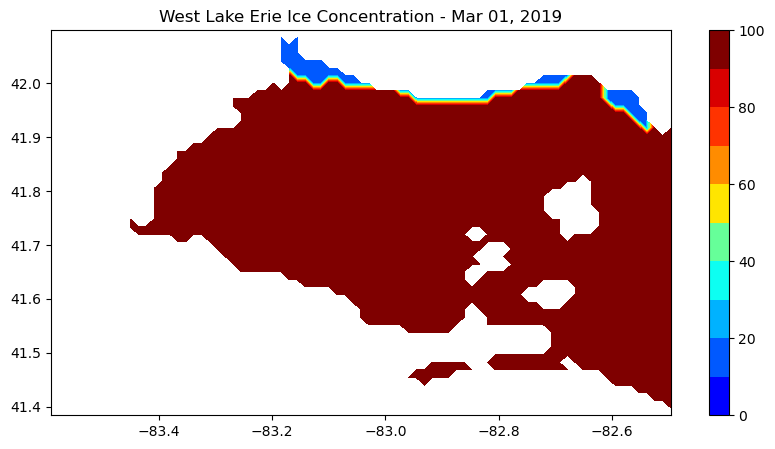
Let’s compute the daily mean over the west Lake Erie region:
res=np.nanmean(nan_ice_concentration,axis=(1,2))
resarray([0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], dtype=float32)Let’s plot the time-series (from 2019-03-01 to 2019-03-31):
for i, date in enumerate(dates):
if date.strftime("%Y-%m-%d") == "2019-03-01":
print(i, date)
if date.strftime("%Y-%m-%d") == "2019-03-31":
print(i, date)5872 2019-03-01 12:00:00
5902 2019-03-31 12:00:00print(res.shape)(7146,)plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
plt.scatter(dates[5872:5902+1],res[5872:5902+1])
#degree_sign = u"\N{DEGREE SIGN}"
plt.ylabel('Ice Concentration (%)')
plt.xlim(dates[5872], dates[5902+1])
plt.xticks(dates[5872:5902+1],rotation=70, fontsize=10 )
plt.show()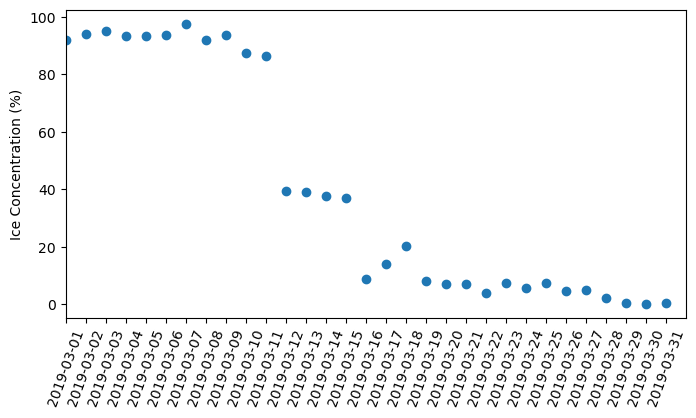
!jupyter nbconvert --to html GL_python_tutorial4.ipynb[NbConvertApp] Converting notebook GL_python_tutorial4.ipynb to html
[NbConvertApp] Writing 313369 bytes to GL_python_tutorial4.html